Neck (CT) PRINT
Last updated: 6/13/2022
What changed: extend inferior slices to below aortic arch in order to visualize course of recurrent laryngeal nerve
History: lump, bump, palpable abnormality, swelling, general screen, airway anomaly.
Key tips:
- For clinical mass or palpable abnormality, place a non-metallic marker on the skin overlying the mass so the radiologist knows where to look.
- Use of dose modulation is mandatory.
- Do not scan CT neck without followed by CT neck with contrast unless directed to do so by a radiologist or unless using salivary gland protocol.
Coverage Examples:
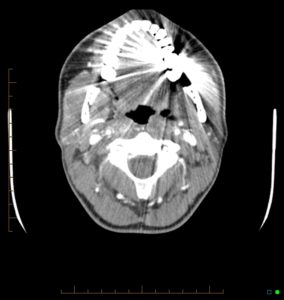
If there is artifact from dental amalgam (axial image below), run a butterfly scan at a different angle through the area. This will allow for detection of lesions in the base of tongue and palatine tonsils (eg. squamous cell carcinoma).
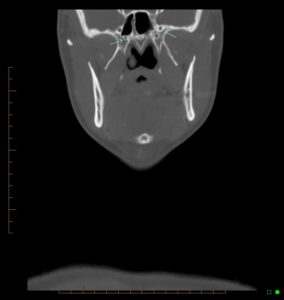
On coronal, must be able to see skull base foramina (arrows).

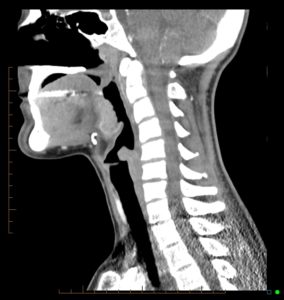
On Sagittals, top should be the planum sphenoidale / sella.